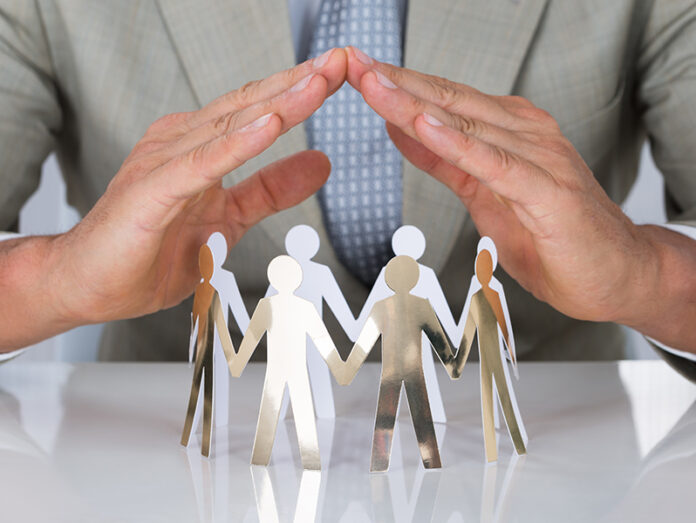
As a business owner, you need to understand the different types of business insurance available to SMEs.
“Many businesses do not purchase business insurance coverage as a means of saving on expenses. But one needs to ask whether a few hundred rands is worth saving versus the total expenditure required to repair the damages caused by unforseen events,” says Khumo Mahuma, Founder, Director and Representative of Health and Rands Business and Financial Consulting.
Business owners and entrepreneurs can plan for the sustainability of the business by addressing business continuity plans, which are driven by the level of insurance and assurance of the business, the business owner, partners and the employees, even going to an extent of the clients and customers and its products and services. In every business planning process, it is critical to mitigate company-specific risks and risks that are influenced by (PESTEL) Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors. Adequate insurance is required and start-ups should ensure that they engage professionals to develop a business plan that factors in their insurance and assurance requirements.
The appropriate choices will depend on the kind of business, its size, and its potential risks:
Business Insurance
This is aimed at insuring the business operations, business assets, product and services offerings and human capital operating within the business to ensure continuity and avoid liability. It is important to to consider your companies’ unique risk factors.
The following are some of the covers that are important to consider:
- Business Insurance: Insurance of movable and fixed assets.
- Business Overhead Expense: Insurance cover taken by a business owner to cover business overheads should they not be in a position.
- Business Owner’s Insurance: A business owner insurance policy offers SMEs broad protection against financial loss. If their property is damaged by fire or flooding, for example, then the insurance company may pay the cost of repairs. Among the risks that may be covered in a business owner’s policy are: Fire, Flooding (pipe bursts), Other sources of property damage, Theft, Bodily Injury, and Business interruption for specified reasons.
- Commercial Insurance: plans are designed to protect small businesses from injury claims, cyber attacks and other liabilities.
- Professional Malpractice Insurance: Professionals in fields like Medicine, Dentistry, Law, Accounting, Advertising, Financial Planning, Occupational therapy, Computer analysis, Journalism, Psychotherapy, and Real estate that give advice and/or provide services require professional malpractice/professional indemnity insurance to protect themselves from substantial liability in the event of a lawsuit for material liability they might have caused their clients.
- Product Liability Insurance: This type of insurance, obtained at additional cost, may be a necessity if you sell a product that has the potential to injure a user. If you sell a product that injures someone—even if you did not design, manufacture, or distribute the product—then you may have legal liability that should be covered.
Business Owner Insurance
This is aimed at ensuring continuity of the business in an instance where the business owner(s) is/are unable to continue working in or on the business. Events that prompt this include death, temporary or permanent disability or critical illness. When such an event happens, the business must continue to run.
- Key man Insurance: insurance the business takes on the life of the key person (the critical skilled person) to replace him with another equally or more skilled person in the event when they cannot continue to participate in performing their role, and the business continues to run.
- Buy and Sell insurance: The kind of insurance business partners take on each other so that if one of them is unable to continue with their participation in the business, insurance pays them or their beneficiaries, and the remaining partner(s) take(s) over their part of the business and the business continues to run.
- Contingent Liability Insurance: If a business takes a loan, the business partner(s) will need to take an insurance cover equivalent to that loan. If any of the partners cannot continue with their participation due to death, disability or severe illness, insurance settles their loan, and the business continues to run.
Human Capital Insurance (Employee benefits)
These are umbrella/group benefits structured and offered by various insurance providers an employer takes on behalf of their employees to address various risks. They may include, among others:
- Group death benefits
- Group disability benefits (temporary and permanent disability)
- Group sever illness benefits
- Group funeral benefits
- Group Child Education Benefit
- Group spouse cover
Personal Insurance
Whether you are a business owner, an employer or an employee, you need to build a comprehensive personal portfolio plan.
Your personal portfolio should address the risks you are potentially facing when you are alive, actively earning a salary before you retire, after you retire, or when you are ill, disabled, critically ill or dead. Your life or the lives of your family should not change for the worst during and after any of the life stages mentioned above.
“If you run a business, you need to discuss your needs with an accredited insurance broker and to adequately address and cover all potential risks you and your business might be facing. It is the duty and responsibility of your broker to ensure that you know what you are covered for and that regular reviews of your cover are done to adapt to your changing circumstances,” Mahuma advises.